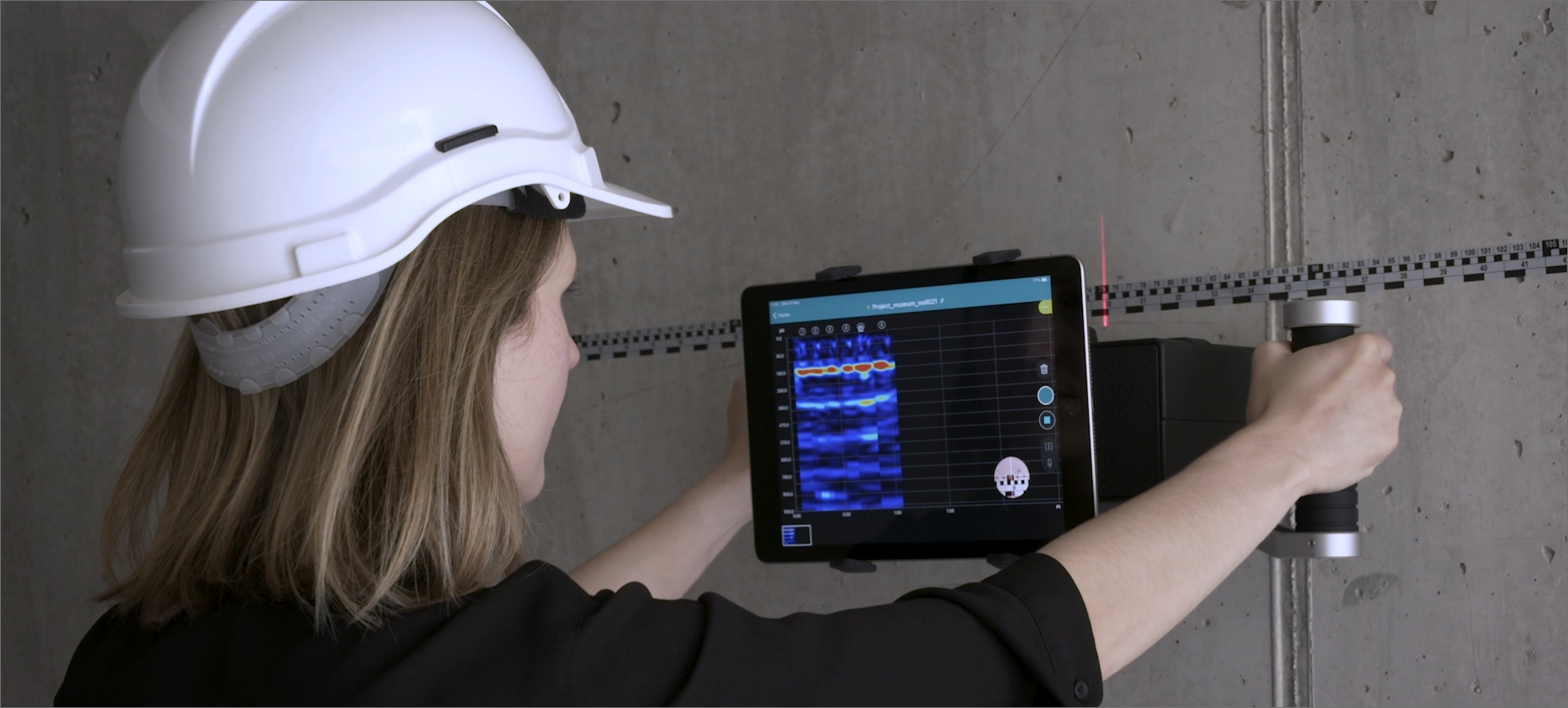
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) for concrete is a set of assessment methods that evaluate the integrity and quality of concrete structures without causing damage. These techniques include ground-penetrating radar, rebound hammer, ultrasonic pulse velocity, and ultrasonic echo testing methods. NDT enables the detection of internal flaws, voids, cracks, and corrosion within concrete, providing valuable insights into its structural health. By identifying potential issues early, NDT helps ensure the safety and durability of buildings, bridges, and infrastructure. NDT is widely used in construction and maintenance to assess concrete without destructive sampling. This helps minimize costs and disruptions while promoting the longevity and safety of concrete structures.
Our comprehensive range of testing methods ensures accurate and reliable results for all your concrete testing needs. We can assess the condition of concrete structures and to detect and accurately map any object or material that may be embedded within concrete, including but not limited to the following non-destructive testing techniques:
- Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR)
- Schmidt Hammer Test
- Impact Eco Test
- Ultrasonic Pulse Velocity (UPV) Test
- Ultrasonic Pulse Echo (UPE) Test
- Crack Evaluation
- Pile Integrity Test (PIT)
- Resistivity Test
- Corrosion Test
Concrete Confidence: Non-Destructive Excellence, Engineering Peace of Mind.
KR Engineering is a leading provider of non-destructive concrete testing services across Canada, in Alberta, British Columbia, and Ontario. We provide comprehensive non-destructive testing services for concrete structures, which include comprehensive inspection methods for determining thickness of walls and floors, identifying voids, delaminations, honeycombs, analyzing cracks, and corrosion potential. We use advanced technology and techniques, ensuring reliable service and safe access to challenging areas. Our expertise makes us a trusted provider and partner for industrial projects, offering effective solutions to maintain structural integrity and safety across various sectors.
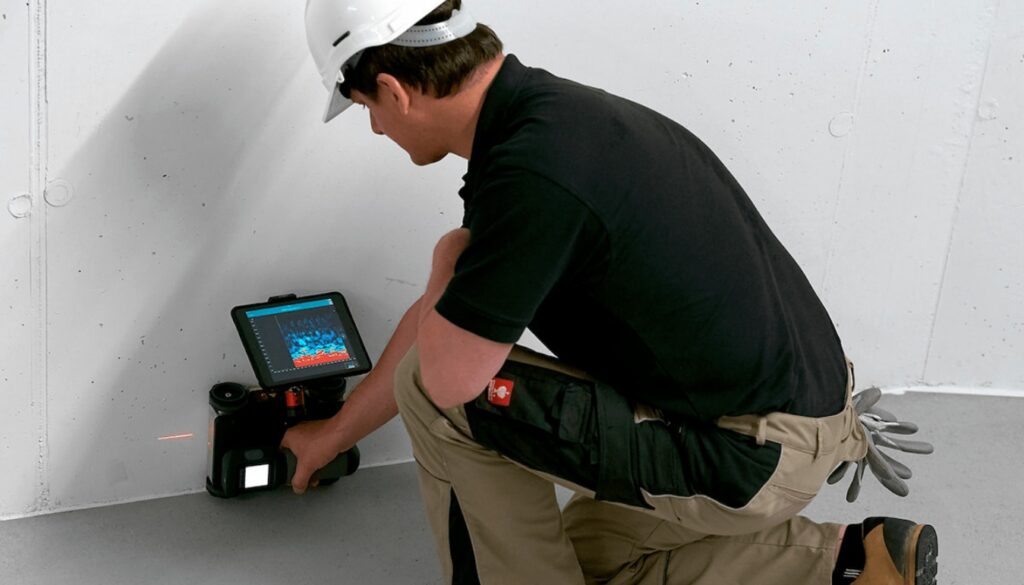

Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR) For Concrete
Rebar scanning is performed using ground-penetrating radar (GPR) or electromagnetic induction (EMI) techniques. GPR works by sending radar waves into the concrete and measuring the reflection of the waves from the rebar, while EMI uses electromagnetic fields to detect the presence and position of the rebar. The data obtained from these tests are used to map a detailed view of the rebar layout in concrete walls, slabs, bridges, and other structures. The size, spacing, and orientation of the rebar are also determined from these tests. Rebar scanning is an important step in construction, maintenance, and repairs, as it helps to ensure adequate rebar placement and the reliability of a structures continued use. As well, due to its high accuracy, GPR is a cost-effective and timely way to cover large areas of a job site.
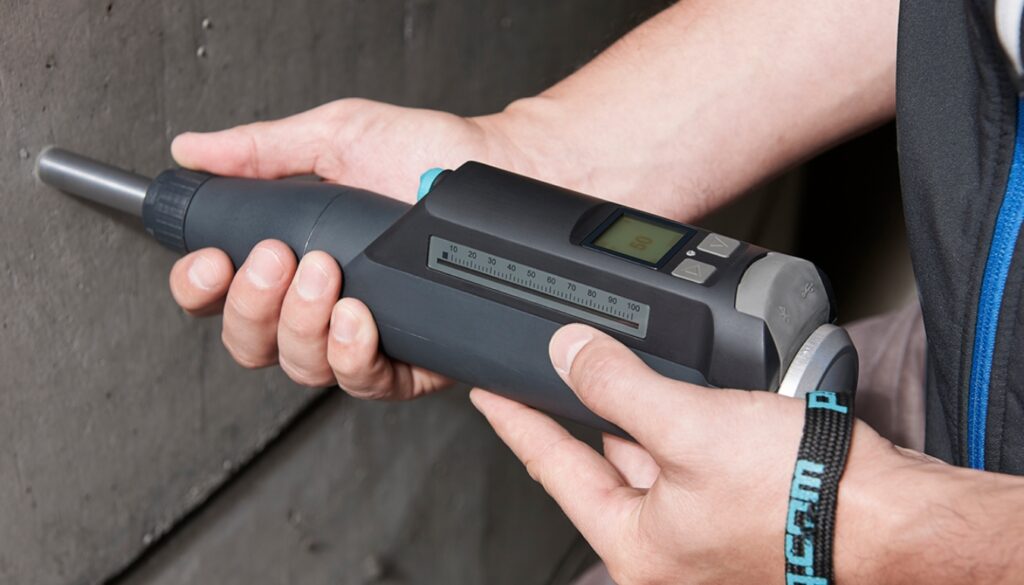

Schmidt Hammer Test
The Schmidt Hammer, also known as the Rebound Hammer, is a non-destructive testing device used to estimate the compressive strength of concrete and other materials. The device works by measuring the rebound of a spring-loaded mass when it strikes a surface, which is then used to estimate the hardness and compressive strength of the material. The Schmidt Hammer is a quick and reliable way to obtain an approximate measure of concrete strength and is widely used in construction and engineering applications. The Schmidt Hammer test is an appropriate technique for conducting the following items:
- Concrete compressive strength estimation
- Ensuring uniformity in concrete construction
- Ensuring proper concrete curing before removing the formwork
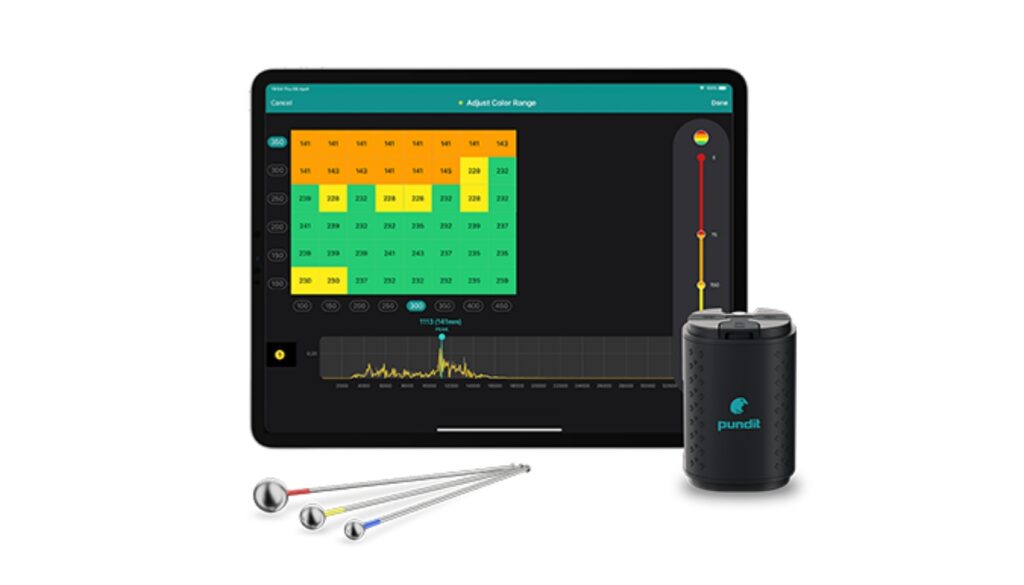
Impact Echo Test
The Impact Echo Test is a non-destructive evaluation technique used to assess concrete structures. It involves striking the concrete with a lightweight impactor, generating stress waves that travel through the material. Echoes from defects and voids are recorded by a microphone and analyzed with specialized software. By measuring the time intervals between impacts and echoes, the test determines concrete thickness and identifies defects. This method is non-invasive, making it ideal for bridges, buildings, and pavements, as it helps detect issues early, enabling timely repairs and enhancing the safety and longevity of concrete structures. The impact echo is a suitable method for carrying out the following tests:
- Assessing the length of piles
- Assessing the quality of piles to determine pass or fail
- Mapping of concrete slab thickness
- Detection of defects such as voids or delaminations
- Conducting inspections of assets such as buildings, bridges, and piles
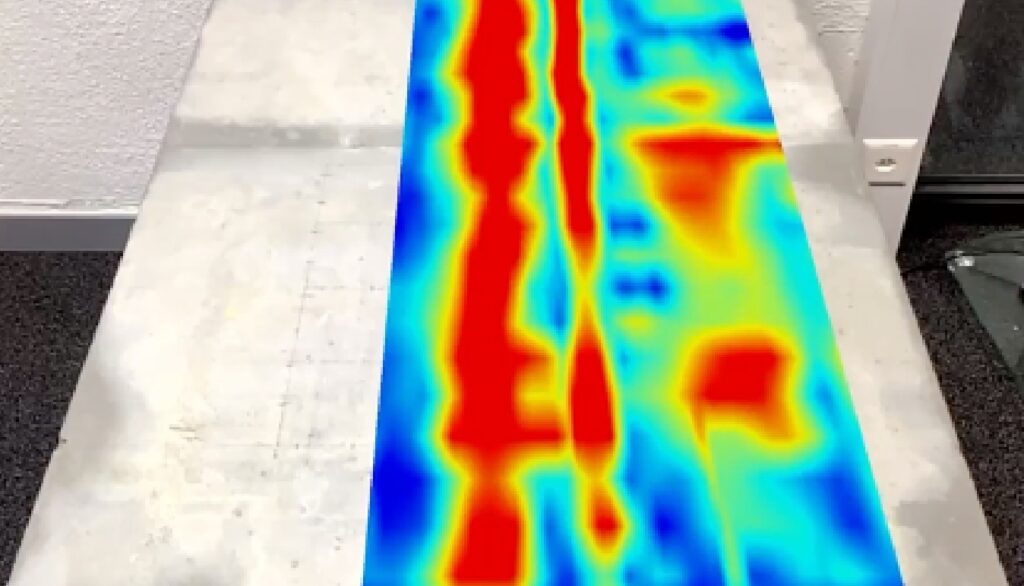
Ultrasonic Pulse Velocity (UPV) Test
Ultrasonic Pulse Velocity testing is a non-destructive method used to evaluate the homogeneity and integrity of concrete structures. It works by measuring the time it takes for an ultrasonic pulse to travel through the concrete and back. The velocity of the pulse is proportional to the density and elasticity of the concrete, and deviations in the velocity can indicate the presence of cracks, voids, or other defects. UPV testing is a relatively fast and efficient method for evaluating large concrete structures and is commonly used in the construction and engineering industries to assess the quality and durability of concrete structures. The test is performed by placing transducers on the surface of the concrete, and the data obtained is used to generate a comprehensive report on the condition of the structure. The results of UPV testing can be used to make decisions about the repair or maintenance of concrete structures, and to ensure that they are safe and stable for continued use. The UPV testing method is appropriate for the following applications:
- The correlation between the compressive strength of concrete and rocks
- Mapping of concrete for concrete thickness
- Estimating the strength of concrete using the SONREB (Sonic and Rebound) method
- Quality assessment.
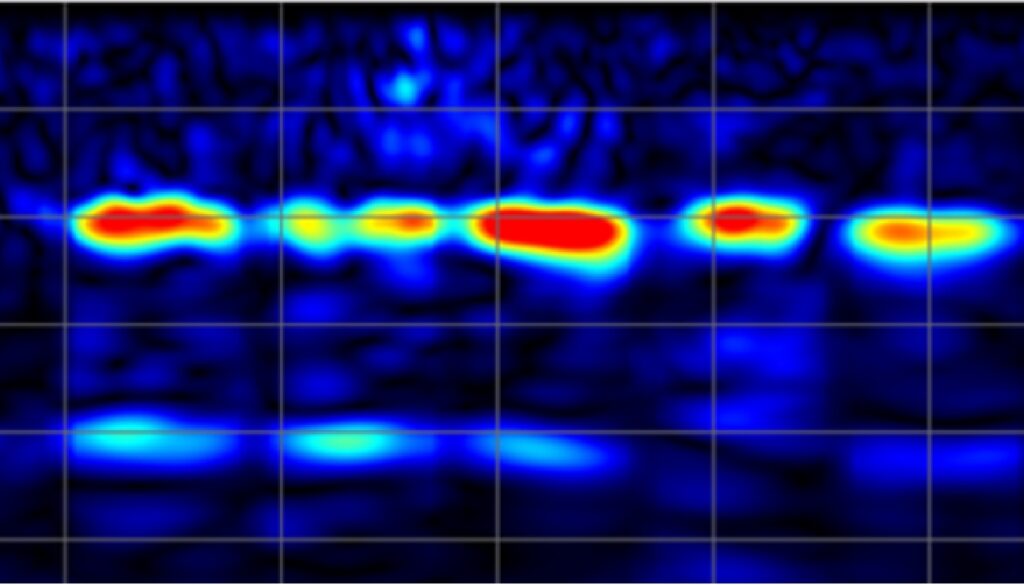
Ultrasonic Pulse Echo (UPE) Test
Ultrasonic Pulse Echo testing is a non-destructive evaluation method used to inspect concrete structures for cracks, voids, and other defects. The test works by sending an ultrasonic pulse into the concrete and measuring the
time it takes for the echo to return from any defects in the material. The amplitude and frequency of the echo can be used to determine the size and location of the defects, such as voids, honeycombs, delamination, and cracks and to assess the overall integrity of the concrete structure. UPE testing is commonly used in the construction and engineering industries to inspect concrete structures for signs of degradation and to determine the need for repairs or maintenance. The test is typically performed using specialized equipment, including ultrasonic transducers and data acquisition systems, and can be performed on large concrete structures in a relatively short period of time. The results of UPE testing can be used to make informed decisions about the maintenance and repair of concrete structures, and to ensure that they are safe and stable for continued use. The UPE testing method is appropriate for the following applications:
- Location of subsurface defects of concrete
- Measurement of thickness of concrete elements
- Determination of concrete pulse velocity for homogeneity and strength estimation
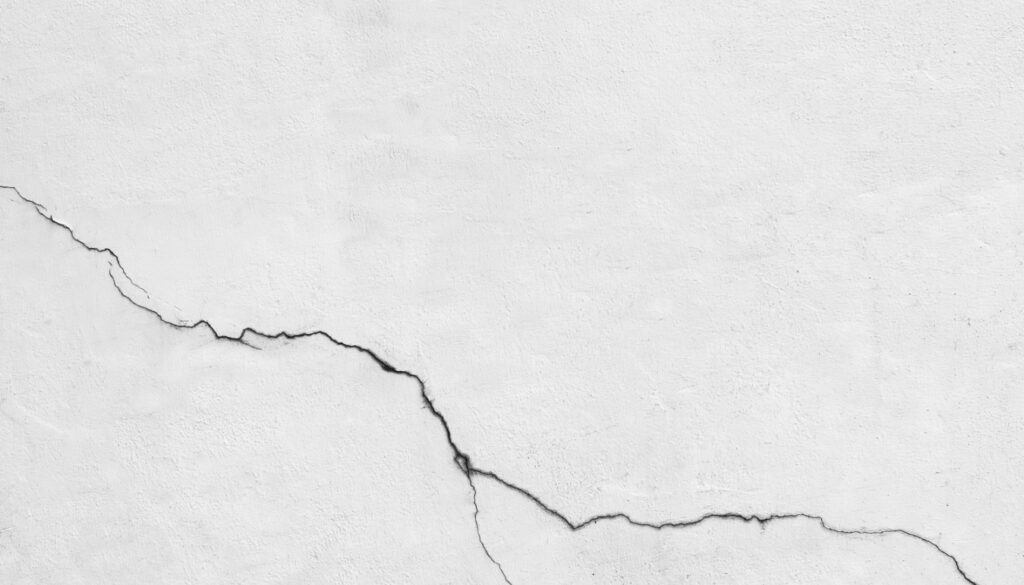

Crack Evaluation
Crack Evaluation for concrete is a method used to assess the condition of concrete structures and to determine the presence and severity of cracks. The evaluation is performed by visually inspecting the concrete and measuring the size, length, and orientation of any cracks that are present. Crack evaluation is an important step in the assessment and maintenance of concrete structures, as it helps to identify potential problems before they become serious and to ensure that structures are safe and reliable for continued use.
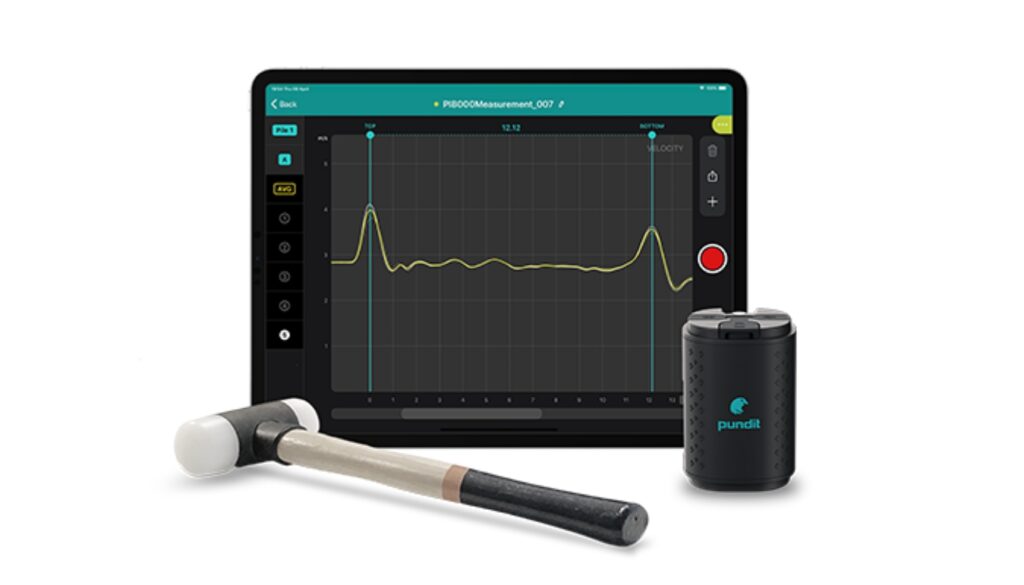
Pile Integrity Test (PIT)
Pile Integrity Test typically involves the use of impact, sonic, or pulse-echo testing methods to evaluate the pile. Impact testing involves striking the pile with a weight and measuring the resulting waves, while sonic and pulse-echo testing involve transmitting sound waves into the pile and measuring the resulting echoes. The data obtained from these tests can be used to determine the condition of the pile and to identify any defects such as necking and bulging in the pile shaft. PIT is an important test for evaluating the deep foundation systems, as it helps to ensure that piles are installed correctly and can support the loads they are intended to carry.
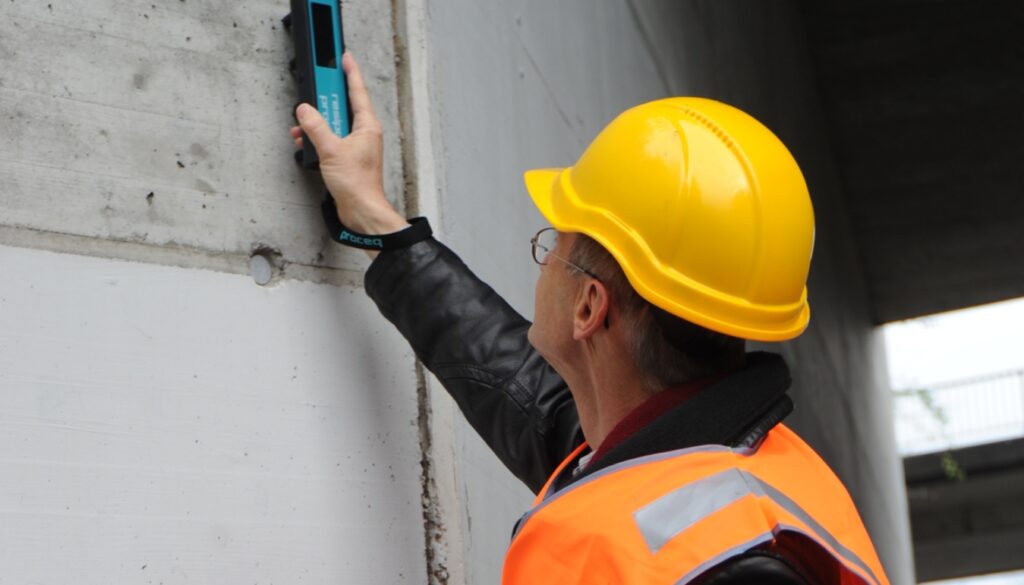

Resistivity Test
Concrete resistivity testing is a non-destructive method used to assess the electrical conductivity of concrete structures. It measures the ability of concrete to conduct electrical currents, which is crucial for evaluating its durability and corrosion resistance. By analyzing resistivity values, engineers can predict the likelihood of corrosion in reinforcement and make informed decisions regarding maintenance and repair. This test involves applying a voltage to electrodes embedded in the concrete and measuring the resulting electrical resistance, providing valuable insights into the concrete's quality and long-term performance.
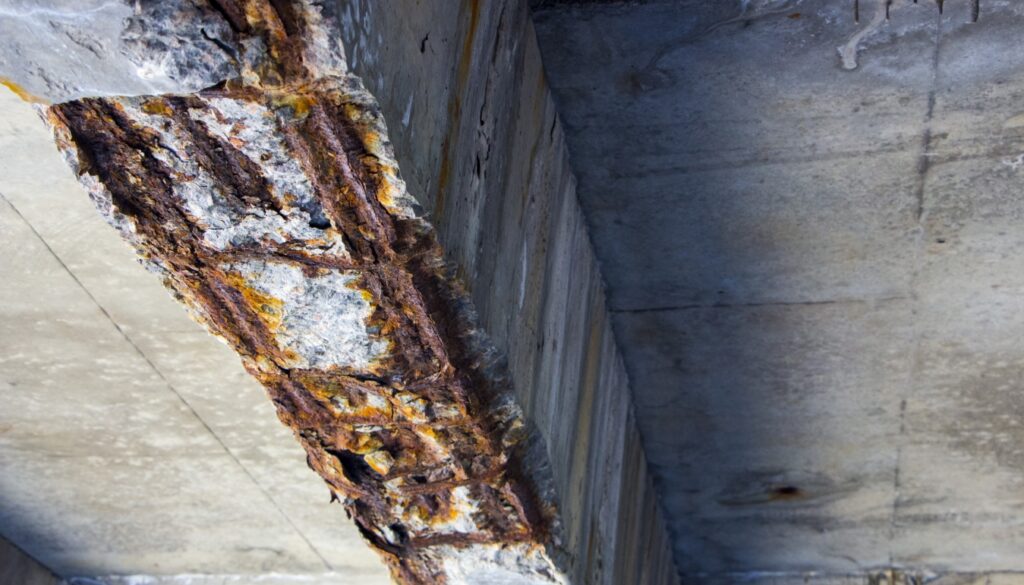
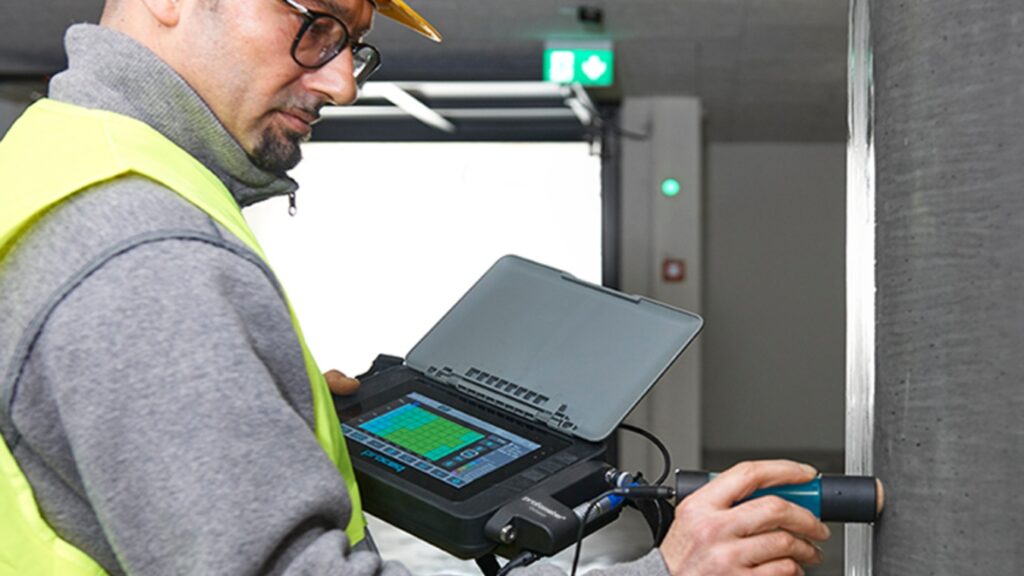


Corrosion Test
Concrete corrosion potential testing is an important step in the assessment and maintenance of reinforced concrete structures, as it helps to identify potential problems before they become serious and to ensure that structures are safe and reliable for continued use. The results of concrete corrosion testing can be used to determine the presence of corrosion in the reinforcing steel, which can cause concrete cracking, spalling, and loss of structural integrity and make decisions about the repair and protection of concrete structures, and to ensure that they are preserved for future generations. There are several methods for concrete corrosion testing, including electrical resistance, half-cell potential, and chloride ion penetration tests. Electrical resistance testing measures the resistance of the reinforcing steel to determine the presence of corrosion, while half-cell potential testing measures the electrical potential of the steel to determine the likelihood of corrosion. Chloride ion penetration testing is useful for the following applications:
- Detecting corroded sections in reinforced concrete structures
- Estimating the corrosion potential of rebars
- Investigating the causes of structural failures
- Assessing the effectiveness of corrosion repairs

